Summer generally provides a bit of time for reflection and gathering of thoughts. It also marks the start of the final phase of the current JISC Distributed Virtual Learning Environments (DVLE) programme. For the five institutionally based projects, this summer has provided a short break before some major implementations and evaluations get underway in the new semester. This post summarizes some of the developments and future plans as outlined by the projects in their recent interim reports.
To give a bit more context the original call for funding for the institutional projects specifically asked for bids that would:
” . . .review their virtual learning environment and related systems to establish to what extent they meet the current and projected needs of the wide range of users in the institution and beyond, and implement technical work to widen the range of functionality the VLE can provide in an interoperable way.”
Which would lead to a set of deliverables including:
“• Enhancing the flexibility of VLEs to meet new and developing user requirements and to permit future expansion and changes.
• Demonstration of a range of architecture models for composing institutionally delivered learning environments.
• Guidance on, and models for, expanding VLE functionality and delivering it in different ways to meet institutional needs.
• An increased number of high-quality sharable widgets and applications made available to common web platforms in UK institutions, and an easier process of deploying them.”
So what progress is being made?
ceLTIc, University of Edinburgh
Progress continues with deployment of LTI connectors across a range of platforms including BB, Pepplepad, Elgg. You can get more of a feel for what the project has achieved so far from their recent presentation at our IMS LTI and LIS in Action Webinar. The project are now entering their evaluation phase which aims to “explore the impact of the implementation of LTI connectors with a VLE and four applications: Elgg, WebPA, PebblePad and Learning Objects in a number of higher education institutions from the perspective of:
tutor; developer; e-learning support; administrator.” More information about the evaluation methodology can be found on the project blog.
DEVELOP, University of Reading
The DEVELOP (Developing and Enhancing Virtual Learning Environments and E-Learning Options) team at Reading have primarily been exploring the extension of their BlackBoard VLE to allow greater pedagogic flexibility and their portfolio provision so that it can be used for teaching and assessment purposes. Scoping documents for their widget development (Tagging and recommender, portfolio, ASSET Video, content) are available from the project blog. At the moment, the widgets are all at various stages of development and user testing. The user evaluation and testing are part of the rapid prototyping approach the team are using (you can read more about the technical evaluation part of this process in this post. These evaluations will form the basis for a set of case studies around the effectiveness of each of the widgets. The case studies will be based on the templates created at Reading as part of another project JISC funded project, OULDI, which is part of the Curriculum Design Programme. The team have also been working closely with their key internal technical stakeholders to ensure sustainability of developments. The University of Bedfordshire is also testing the video widget.
DOULS, OU
The DOULS (Distributed Open University Learning Systems) team have continued with key user engagement processes to scope, define and specify the set of Google gadgets they are going to develop: Assessment Helper; Forum Recommender; Forums; OU Buddy; Study Planner. Draft gadget functionality specs for each one is available the project blog. The team have also documented their process and have produced a number of useful guidelines relating to usability and accessibility in terms of testing gadgets and overall management of accessibility within a VLE. These are openly available from the blog. The team are continuing to learn the “ins and outs” of working with the Google Apps for Education API for widescale adoption. Again the team are sharing some of their “visions” for potential Google App/Moodle integration and thoughts around potential uses/extensions for the Google start page on the blog. There will be more code releases in September, when they will also start their evaluation. Their interim report is also available for download from the blog.
SLEP, University of Southampton
The SLEP (Southampton Learning Environment Prototype) project is part of a wider institutional wide initiative at Southampton to restructure both its research and teaching and learning environments. As you’d expect from Southampton, open and linked data are central to their approach and the team have used a “co-design” process “made up of a large- scale student survey, smaller focus groups and one-on-one interviews) has revealed a preference for a small number of key services in our initial launch (including email and timetabling).” This process has also surfaced the importance of groups and communities, and the team’s prototype interface design highlights these and makes “ them the lens through which students and staff access all of the data and services of the institution”. The project is now coming out of “stealth” mode with their first round of apps being released in September accompanied by a large scale (c. 1,000 students) user evaluation of their new user interface. More detail on their overall approach and the co-design methodology is outlined in this paper presented at the PLE conference earlier this summer.
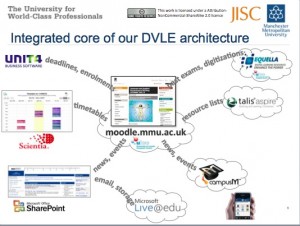
W2C, MMU
The W2C team continue to make good progress with what they often refer as their “megamash up”. The team have made steady progress developing web services including: PC Availability; Fee Status (RSS); WebCT Areas & Announcements (RSS); Library Reading Lists (RSS) & Podcasts (RSS); Integrating Talis Aspire and Equella. Providing this information in a mobile friendly way has had a dramatic impact on the number of hits these services are now getting. The team have been closely monitoring the usage of these services and shared how they collect the data and some of their insights in this post. The team have also been involved in a study of student use of mobile devices with a number of other institutions. Preliminary findings from the on the MMU part of the study are available in this post .
The team have prioritised the development of web services for mobile devices and have been working with oMbiel’s campusM mobile phone product. This has allowed them to rapidly deploy their web-services and create a user feedback loop. The team have also undertaken work in developing open source widgets for their Moodle installation which I’ll refer to later in this post. The W2C project, again is part of a wider institutional change process around provision of teaching and learning and the team have been very pro-active in sharing their “core- plus” model with the rest of the programme and the wider community.
Reflections
The CETIS Distributed Learning Environments briefing paper was a key starting point for the programme, and particularly for the institutional strand, JISC wanted to find out the key institutional infrastructure issues are surrounding more flexible creation distribution of apps/gadgets/widgets and how data can be shared and re-used effectively.
Again going back to the funding call: “ The following technical approaches are of particular interest:
• Widget platforms external to the VLE displaying content from a range of sources including the VLE.
• Plug-ins to the VLE or other institutional web platform demonstrating the use of open educational standards such as IMS LTI (learning tools interoperability).
• The VLE providing some of its data and functionality as widgets/and or plug-ins to be consumed in other environments.
• Enabling access to particular research equipment in VLEs via widgets.
• Identity and access management approaches, such as OAuth.
• Approaches which illustrate innovative creation, use and consumption of data sets (including linked data ) sets across multiple platforms.”
Security has been and continues to be a key concern for projects (as highlighted in this post from Mark Stubbs after the programme start up meeting last September). Accessibility is also a concern, and it’s probably fair to say that the DOULS and others at the OU have had to spend more time than they probably first envisaged ensuring that their Google apps provision met required accessibility guidelines.
However there have been some quick wins for example W2C have been able to accelerate their mobile app deployment using an external partner which freed up the team’s time to work on developing web-services. We are also beginning to get a far greater understanding of student mobile device ownership and indeed from all the user engagement across the projects a greater understanding of the key data/services which staff and students actually want and use regularly.
In terms of standards/ specifications we have a stalwart supporter of the IMS LTI approach from Stephen Vickers at the ceLTIC project who clearly thinks the IMS way is a win, win, win scenario. There is still some resistance to implementing LTI in other projects – partly due to their unfinished status. Reading are keeping a watching brief on developments and are concentrating on developing widgets they know will work in their VLE. Whereas Southampton prefer to work with more conventional, non education specific web service approaches. However the recent announcement from IMS that they are now merging the development of full and basic LTI into one specification may start to convince more potential adopters. Once again the security question raises its head. Whilst there seems to be more convergence across the IMS, Open Social and Wookie development communities around the use of services such as OAuth, and the development of data handling process which sh/could start to allay common concerns around security of sensitive data such as assessment information etc. However, there is still probably a need for quite a dramatic culture shift within institutional provision and access before OAuth is widely adopted across the sector.
The programme has also afforded the opportunity for projects to explore the W3C Apache Wookie (Incubating) approach to the building and deployment of widgets. Our widget bash provided hand on opportunities for developers to get started building (and repurposing their own apps) wookie widgets. Despite the (relative) ease of building widgets, there has been some articulation surrounding concerns around the institutional deployment of a wookie widget server see this post from the W2C project. There continues to be an appetite for a stable sandbox/test server that projects could experiment with. This has been discussed before through our widget working group (pre-cursor to the DVLE programme) and it is something we at CETIS do recognise. Unfortunately we aren’t in a position to guarantee stability of any such service, and so we have being advocating a community based solution (perhaps augmented with a bit of funding from JISC). This is bound to be something we return to at the end of the programme once the projects have completed their reviews of their approaches and we can get a more informed view from across the programme.
There is also the question of where widgets/apps/gadgets should be accessed from after the projects finish. Should the code be available only via project websites? Do we need think about developing education app store (again this brings up similar issues as the wookie test server). One potential interim measure we are starting to investigate is the use of the JISC Design Studio which is primarily being used to share outputs from the Curriculum Design and Delivery programmes, but there are plans to use it to share other programme outputs too.
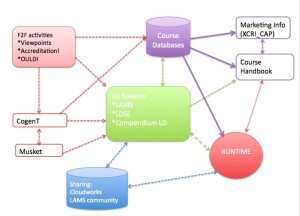
In the final stage of the funding cycle, the projects will be reflecting more on their infrastructure and how they relate to the models outlined in the CETIS DLE briefing paper. Both DEVELOP and W2C are seeing alignment with Model 2 “plug-ins to existing VLEs”.

screen shot of DLE Model 2
W2C have begun to articulate their model in a some more detail in this post.
Over the coming months as evaluations begin in earnest, it will be interesting to see any convergences of approaches/models start to appear, and to explore what kind of affordances the projects distributed learning environments have to offer over traditional approaches.
More information about the projects and the programme support activities can be found on the CETIS wiki. There is also a public netvibes page with feeds from all the project blogs.
The timeline below also gives another view of programme activity through aggregated tweets using the programme hashtag #jiscdvle and with an RSS feed from the related Learning Platforms topic page on the CETIS website.