Data,to coin a phrase from the fashion industry, it’s the new black isn’t it? Open data, linked data, shared data the list goes on. With the advent of the KIS, gathering aspects institutional data is becoming an increasing strategic priority with HE institutions (particularly in England).
Over the past couple of weeks I’ve been to a number of events where data has been a central theme, albeit from very different perspectives. Last week I attended the Deregulating higher education: risks and responsibilities conference. I have to confess that I was more than a bit out of my comfort zone at this meeting. The vast majority of delegates were made up of Registrars, Financial Managers and Quality Assurance staff. Unsurprisingly there were no major insights into the future, apart from a sort of clarification that the new “level playing field” for HE Institutions, is actually in reality going to be more of a series of playing fields. Sir Alan Langlands presentation gave an excellent summary of the challenges facing HEFCE as its role evolves from ” from grant provider to targeted investor”.
Other keynote speakers explored the risks, benefits exposed by the suggested changes to the HE sector – particularly around measurements for private providers. Key concerns from the floor seemed to centre around greater clarity of the status of University i.e. they are not public bodies but are expected to deal with FOI requests in the same way which is very costly; whilst conversely having to complete certain corporation tax returns when they don’t actually pay corporation tax. Like I said, I was quite out of my comfort zone – and slightly dismayed about the lack of discussion around teaching, learning and research activities.
However, as highlighted by John Craven, University of Plymouth, good auditable information is key for any competitive market. There are particular difficulties (or challenges?) in coming to consensus around key information for the education sector. KIS is a start at trying to do exactly this. But, and here’s the rub, is KIS really the key information we need to collect? Is there a consensus? How will it enhance the student experience – particularly around impact of teaching and learning strategies and the effective use of technology? And (imho) most crucially how will it evolve? How can we ensure KIS data collection is more than a tick box exercise?
Of course I don’t have any of the answers, but I do think a key part of this is lies in continued educational research and development, particularly learning analytics. We need to find ways to empowering students and academics to effectively use and interact with tools and technology which collect data. And also help them understand where, how and what data is collected and used and represented in activities such as KIS collection.
As these thoughts were mulling in my head, I was at the final meeting for the LDSE project earlier this week. During Diana Laurillard’s presentation, the KIS was featured. This time in the context of how a tool such as the Learning Designer could be used to as part of the data collection process. The Learning Designer allows a user to analyse a learning design in terms of its pedagogical structure and time allocation both in terms of teaching and preparation time, as the screen shot below illustrates.
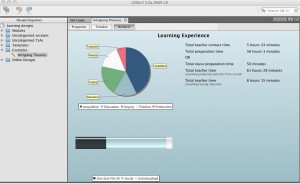
The tool is now also trying to encourage re-use of materials (particularly OERs) by giving a comparison of preparation time between creating a resource and reusing and existing one.
The development of tools with this kind of analysis is crucial in helping teachers (and learners) understand more about the composition and potential impact of learning activities. I’d also hope that by encouraging teachers to use these tools (and similar ones developed by the OULDI project for example) we could start to engage in a more meaningful dialogue around what types of data around teaching and learning activities should be included in such activities as the KIS. Simple analysis of bottom line teacher contact time does our teachers and learners an injustice – not to mention potentially negate innovation.
The Learning Designer is now at the difficult transition point from being tool developed as part of a research project into something that can actually be used “in anger”. I struck me that what might be useful would be tap into the work of current JISC elearning programmes and have one (or perhaps a series) of design bashes where we could look more closely at the Learning Designer and explore potential further developments. This would also provide an opportunity to have some more holistic discussions around the wider work flow issues around integrating design tools not only in the design process but also in other data driven processes such as KIS collection. I’d welcome any thoughts anyone may have about this.
hi
can you please keep me informed about any more design bashses you hold especaily around work flow as most Stage2 Course Data projects will be investigating these. Or anything you or anyone else at CETIS does about the KIS?
Thanks
Ruth Drysdale
JISC Exec
Hi Ruth
Yes of course
S