Continuing from my last post, the next part of the programme technical journey focuses on the Cluster B projects: Co-educate, SRC, P3 who had similar objectives in terms of organisational change.
SRC
*Project Prod entry
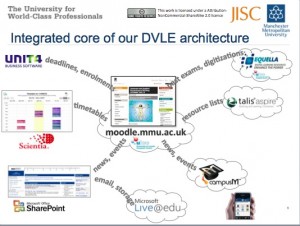
In terms of organisational change, SRC (Supporting Responsive Curricula) is part of larger set of project EQAL which is radically changing the way the MMU provides learning services (in the broadest sense) to its students. Other JISC funded initiatives e.g. the W2C project are connected to this major organisational change, of which SOA approaches is key. Professor Mark Stubbs’ keynote presentation at this years CETIS conference gives an overview of their overall technical approach.
MMU is in the processes “introducing a new curriculum framework, new administrative systems and processes, revised quality assurance processes and new learning systems to transform the student experience” and the SRC project has been at heart of the complete revision of all undergraduate courses, through developing a processes and workflows for a common curriculum database which feeds into a range of other learning services a part of their “corePlus” learning environment provision.
All course module and assessment structures have been completely revised (starting with first year and now extending to 2nd and 3rd). A new course database is now being populated using a common set of forms which provide a common set of tags (including competencies) and unique identifiers for courses which can be used a part of a wider set of “mash up” activities for students to access. When redesigning the course database, extensive stakeholder engagement and mapping was undertaking (using Archimate) in relation to QA processes which formed a key part of the project’s baseline report. A case study details this work and this blog post provides a summary of the new course documentation and QA processes including a map of the new peer review process.
A key part of the project has been to explore effective ways for students to showcase their experience and abilities to employers. A number of systems have been explored and an institutional e-porfolio strategy produced. A decision has now been taken to provide institutional support for Mahara, beginning in September 2013.
In terms of standards/specifications, this being MMU, XCRI is integral to their systems but hasn’t been a core part of the project. Like other projects, the institutional demand for xcri is still not widespread. However members of the team are key to developments around the integration (and thereby extension) of XCRI into other specifications such as MLO and various competency related initiatives.
Now the major technical implementations have been implemented, the team are now focussing on the wider cultural changes, engagement with staff e.g. the development of the Accrediation! Board game which I’ve written about before, and evaluation.
Coeducate
*Project Prod entry
“Coeducate is a cross institutional project that will focus our staff on a re-engineering of the professional curriculum. It will develop new processes and technical systems to support curriculum development and design that start with the needs of the learner and their organisation. This will be negotiated and delivered in partnership and with full recognition of in-work and experiential learning.”
Coeducate, has taken an the almost opposite approach to MMU in terms of a top down approach to creating and managing new courses. They have connected their SITS database with their new Moodle installation see this blog post for an overview, but unlike MMU do not have a set of course templates, or the same level of automatic course population. Instead, staff now have more flexibility in terms of creating courses suited to their specific needs, as this post and linked documentation describes. The IDIBL framework has also been developing as template for course creation, however the institution has developed an alternative undergraduate curriculum framework. The team have also produced a report on approaches to developing open courses, which again should provide a useful staff development resources.
Following this more bottom up approach, the team have also instigated an series of innovation support network seminars and produced a set of online resources (housed in Moodle) to support staff as new institution validation process are being introduced. Like so many of the projects being caught up in a sea of other institutional change initiatives that aren’t as tightly coupled as MMU, the project has focused effort on providing support to staff to guide them (and in turn the institution) through changes such as course revalidation. The project has been able to to influence and inform institutional strategy to initiatives such as course revalidation through some light weight data analysis of the VLE in terms of course structure, numbers and types of assessment etc.
Over the past year, the team have also been exploring the Business Model Canvas tool in terms of its suitability for learning design planning and/or conceptual modelling. The flexibility of the tool has been identified as a key strength. The team have found other more specific learning design tools such as the LDSE too prescriptive. This post outlines the approach of integrating this tool within Archi (which is being developed by colleagues at the University of Bolton). The tool is currently being trialled with PGCHE students, and again will hopefully provide another design tool for the University and the rest of the community. The team have been using the tool to support staff in course revalidation process, and are lobbying for its adoption into the formal revalidation process.
The team had hoped to do more work on integrating widgets into Moodle for course authoring. However staff issues and a refocus of project priorites has meant that not as much progress on this has been made as originally intended. However, over the last few months the team have been able to build a customisable 8LEM widget (more information and a link to a beta version is available here). The principles outlined in the 8LEM methodology are also the basis for the work of the Viewpoints project, and by the end of this June, it is hoped that there will be at least two versions of the widget available based on the approaches of the Viewpoints project as well as the “vanilla” version.
Bolton has also been successful in gaining funding for one of the JISC Course Data projects and this project will extend work started in Co-educate. The work done through the CoEducate project has help to articulate some of the key requirements for data reporting and practical uses of data collection, including key indicators for retention and drop out.
As with other projects, the challenge for the team is to ensure that the resources and approaches explored and advocated through the project continue to be embedded within institutional frameworks.
Enable
*Project Prod entry
“As a ‘hub’ initiative, the project aims to enable the University to join together its various change initiatives around curriculum development into a coherent and radical overall change process, which will ensure all stakeholder needs are understood, identify overlooked problems areas, and provide a sustainable solution . . .”
The Enable project started out with the vision of connecting and enhancing institutional processes. As with all the other projects, senior management buy-in was always a critical part of the project and a Senior Management Working Group was set up to ensure this buy-in. Part of the wider institutional story has been the relatively high number of changes at senior executive level which have impacted the project. The team have shared their experiences around managing change and information processes.
In terms of technologies, as well as being part of the Design Programme, the project has engaged with a number of other JISC funed initiatives. The team have been an early champion of EA approaches and have been involved with the JISC FSD EA practice group initiative. They have piloted TOGAF approaches in an Archimate pilot. Their experiences of using Archi in for their work in external examiners pilot are summarised in this blog post and embedded slides. Phil Beavouir, the developer of the Archi tool has also posted a thoughtful response to this post. If you are interested in EA approaches , I would recommend both these posts.
The team have also been experimenting with a number of different ways to automate their code build, acceptance, testing and deployment processes. These tools and techniques are being adopted and used in other areas now too. Again the team have promised to share more via the blog, in the meantime a summary of the technologies they are using are detailed in the project Project prod entry.
The team have been looking at Sharepoint and, another example of cross JISC programme fertilisation, were able to gain some of the benefits realisation funding for the Pineapple project to experiment with its software. An overview presentation is available here. The pilot was successful, but, at this point in time, no institutional decision on an institutional wide document management system has been made, so no further developments are being introduced in respect of this work.
The team feel that the EA approaches have “enabled” them to define with stakeholders the key areas to be addressed in terms of developing effective processes. And, have found that having “just enough backing” for developments has been effective. Particularly in gaining senior management buy-in whilst Executive decisions are not possible. The project has been able to illustrate potential working solutions to recognised problem areas. They have also been sharing their experiences of EA extensively with the rest of the sector, through presentations at various institutions.
PC3
*Project Prod entry
“The Personalised Curriculum Creation through Coaching (PC3) project is developing a framework that places coaching at the heart of the personalised curriculum design. Learners will be able to select provision suitable to their needs, construct an award (or module set), access resources and learning support, and negotiate assessment, with structured support from a personal coach. The PC3 Framework will facilitate this process by developing the necessary processes, documentation, training and technological support, within the context of Leeds Met’s flexible learning regulations and systems.”
Again the PC3 project has been on quite a journey over the past three and and a half years. Changes at senior management level have meant that, whilst not changing the underlying principles of the project of using coaching (as explained in its curriculum model ), the project team have had to adapt some of their anticipated approaches and have experienced delays in decisions around key institutional wide provision of technologies.
A major milestone for the project has been decision to adopt PebblePad as the institutional portfolio system. The team acknowledge that there is still work to be done around the integration of resources in the VLE and in Pepplepad, in terms of the user experience of switching between systems. Perhaps Pepplepad’s planned LTI adoption will help mitigate some of these issues.
The project is now reaping the rewards of their early work in staff development and are now working increasingly to support students, and their use of technology whilst implementing the PC3 coaching methodology. The approach is now embedded into the Sport Business Management Degree programme (see this post for more information) and students are playing an increasingly important role as coaching ambassadors.
Earlier in the project the team had created a number of video based resources around coaching. Now they are supporting students in the creation and sharing of videos as part of their course work and as coaching ambassadors. The team are working with institutional AV staff around developing approaches to creating video resources with students. The project is also planning a conference, where students will be key contributers, and plan to video sessions and make the recordings available as a set of resources.
The team are also seeing increasing use of social media sites such as Facebook for communication and even for running coaching sessions. This has very much been student driven and developments are being monitored with interest.
The team have also been using a number of google products (forms and documents) for sharing of project information and for part of their evaluation by using google forms to collect session feedback.
Where possible, the project are releasing resources as OER. To this end have they have benefited from the experiences of the Streamline project which was funded through the JISC/HEA Academy OER programme. Institutionally there has been a significant development around workflow of OERs with the institutional repository and the JORUM national repository that the project has benefited from. Again another example of cross programme sharing of experience.
So, another set of projects with common aims but very different approaches to organisational change. In many ways, a top down approach as exemplified by MMU may well be the most effective way to gain widespread adoption. However, MMU have benefited from a more stable senior management perspective and have not had to re-articulate their vision to a different set (or sets) of stakeholders during the project lifecycle as some of the other projects have. Engaging staff and students at different levels, as Bolton and Leeds, have done may well be just as effective in terms of seeing real pedagogical change in the longer term. But whatever approach, the importance of modelling and being able to visualise, and develop conversations and engagement has been central.