Twitter story from the Advances in open systems for learning resources workshop, hosted by CETIS as part of the Repository Fringe 2011 conference.
View “Advances in open systems for learning resources”
Category Archives: learning platforms
“Win, win, win” Are we really there with IMS LTI and LIS?
“Win, win, win” is the mantra from Stephen Vickers (ceLTIc Project, University of Edinburgh) is going to be taking to the Blackboard conference next week. During yesterday’s webinar “IMS LTI and LIS in Action”, Stephen gave an overview of the integrations the ceLTIc project have been able to achieve using basic LTI. And it does seem that we might actually be at a turning point for both basic (and hopefully full LTI) with most of the major VLE vendors now implementing it, and projects such as ceLTIc and EILE (University of Kent), who also presented their work using LTI with Moodle, being able to show real examples of a number of service integrations including blogs, reading lists and streaming servers.
However the biggest battle for uptake and adoption is probably the hardest one – the move from general awareness raising to actually widespread and commonplace use. And, as Stephen pointed out this isn’t just an question of making developers more aware of, but teachers too. So they are the ones asking the question of their VLE teams “do you support LTI” with the knowledge that they can integrate or “mix and match” a lot more “web stuff” into their VLE if the answer is yes. The IT departments should also have the confidence that taking this approach will mean that they can bring more services into their VLE, offer more flexibility to academic staff and not have to worry about a major system upgrade every time they want to add another service.
However these things can take time, and even in the JISC DVLE programme it’s only the ceLTIc project who are actually using LTI. The other projects have noted interest, but as is so often the case, it’s just not quite a priority at the moment, possibly because a number of the projects are dealing with more administrative and non VLE services. Also as the CETIS DLE briefing paper outlined there are a number of potential models for learning environment integration – LTI isn’t the only game in town. On the plus side with more major players now actively involved we might just be on the cusp of seeing some significant advances over the coming year.
The session also included an update from Linda Feng (Oracle) on recent developments with the IMS LIS specification. Again it was encouraging to hear that the working group have been trying to make the spec as usable and flexible as possible. Linda explained how the IMS working group have been developing a set of profiles to allow greater flexibility for implementers and more importantly the profiles will be available, tested and ready before the spec is finalised. Taking this more iterative approach has already allowed the working group to already sort out some element naming gotchas.
Linda also gave a quick walkthrough of a demo of some work Oracle and Blackboard having been doing with SIS data and will be presenting at next week’s BB Conference (an annotated version of the demo is available online). Phil Nicolls (Psydev) then demo’d some bulk data imports from the a cloud service into Moodle.
So all in all a very interesting session with lots of real examples of standards being used in real situations. The recording is available for viewing by following this link.
IMS LTI and LIS in action webinar, 7 July
As part of our on-going support for the current JISC DVLE programme, we’re running a webinar on Thursday 7 July at 2pm.
http://emea92334157.adobeconnect.com/r9lacqlg5ub/
The session will feature demonstrations of a number of “real world” system integrations using the IMS LTI and basic LTI and LIS specifications. These will be provided by the Stephen Vickers from the University of Edinburgh and the CeLTIc project; Steve Coppin, from the University of Essex and the EILE project and Phil Nichols from Psydev.
The webinar will run for approximately 1.5 hours, and is free to attend. More information, including a link to registration is available from the CETIS website.
Widg@t widget building tool
I really like widgets or apps or whatever you want to call those little discrete things you can pop into a web-page, VLE, blog, access on your phone etc. Over the last few years at CETIS we’ve been supporting developments in this area through various activities such as the widget working group, the current JISC DVLE programme and our widget bash earlier this year.
As I’m not a programmer I’m also always on the look out for easy (and preferably free) ways to make widgets. A couple of years ago I thought I had found the answer with Sproutbuilder, but hey-ho as is the way of things they changed their terms of service. As I really didn’t do that much with it, it didn’t seem worthwhile to pay for the service. So, over the past couple of years I’ve been really keen to see some kind of WYSIWYG widget builder funded. We didn’t quite get there within the scope of the DVLE programme, however I’m delighted to report that the latest round of JISC LTIG grants includes the Widg@t project from the University of Teesside.
Building on the work of the ARC team’s excellent WIDE project (one of the DVLE programme’s rapid development projects), Widg@t aims to:
“explore, design, develop and evaluate a WIDGaT toolkit that will support the design, development and sharing of widgets by those directly involved in the teaching and support of disabled students
By engaging pedagogical and technical experts with our intended end users the objective is to produce a WIDGaT authoring tool that enables teachers or students to develop and share bespoke widgets.”
I’m a really looking forward to seeing the developments and final output from this project and hopefully having fun building some widgets again. This time with an open source, W3C standards compliant tool:-) As I’ve commented before, it’s also great to see a continuum of development from across JISC funding and to see pedagogic and technical developments truly working hand in hand.
The team are also looking for community involvement, so if you want to get involved please do contact them, details are on the project website.
Transforming curriculum delivery through technology: New JISC guide and radio show launched
A new JISC guide ” Transforming curriculum delivery through technology: Stories of challenge, benefit and change” has been launched today.
“a mini-guide to the outcomes of the JISC Transforming Curriculum Delivery Through Technology programme, summarises the headline benefits of technology in curriculum delivery made evident by the work of the 15 projects in the programme The outcomes of these projects provide a rich insight into the ways in which institutions and individual curriculum areas can make use of technology to respond more robustly to the demands of a changing world.”
You can access PDF and text only versions of the guide, or order a print copy by following this link
The latest installment of the JISC on Air series, Efficiences, enhancements and transformation: how technology can deliver includes interviews with two projects involved in the programme, (Making the New Diploma a Success and eBioLabs) discussing the impact achieved in two very different contexts and disciplines.
If the mini-guide whets your appetite for more information about the programme, the Programme Synthesis report provides more in-depth analysis of the lessons learned, and further information and access to project outputs is available from Design Studio.
Approaching The Learning Stack case study
Over the past couple of years, I’ve seen a number of presentations by various colleagues from the Univeristat Oberta de Catalunya about the development of their learning technology provision. And last September I was privileged to join with other international colleagues for their OpenEd Tech summit.
Eva de Lera (Senior Strategist at UOC) has just sent me a copy of a case study they have produced for Gartner (Case Study: Approaching the Learning Stack: The Third Generation LMS at Univeristat Oberta de Catalunya). The report gives an overview of how and why UOC have moved from a traditional monolithic VLE to their current “learning stack”, which is based on a SOA approach. NB you do have to register to access the report.
The key findings and recommendations are salient and resonate with many of the findings that are starting to come through for example the JISC Curriculum Design programme and many (if not all) of the JISC programmes which we at CETIS support. The findings and recommendations focus on the need for development of community collaboration which UOC has fostered. Both in terms of the internal staff/student community and in terms of the community driven nature of open source sofware development. Taking this approach has ensured that their infrastructure is flexible enough to incorporate new services whilst still maintaining tried and trusted ones and allowed them the flexibility to implement a range of relevant standards and web 2 technologies. The report also highlights the need to accept failure when supporting innovation – and importantly the need to document and share any failures. It is often too easy to forget that many (if not most of) the best innovation comes from the lessons learned from the experience of failure.
If we want to build flexible, effective systems (both in terms of user experience and cost) then we need to ensure that we have foster an culture which supports open innovation. I certainly feel that that is one thing which JISC has enabled the UK HE and FE sectors to do, and long may it continue.
Communicating technical change – the trojan horse of technology
As the JISC funded Curriculum Design Programme is now entering its final year, the recent Programme meeting focused on effective sharing of outputs. The theme of the day was “Going beyond the obvious, talking about challenge and change”.
In the morning there were a number of breakout sessions around different methods/approaches of how to effectively tell stories from projects. I co-facilitated the “Telling the Story – representing technical change” session.
Now, as anyone who has been involved in any project that involved implementing of changing technology systems, one of the keys to success is actually not to talk too much about the technology itself – but to highlight the benefits of what it actually does/will do. Of course there are times when projects need to have in-depth technical conversations, but in terms of the wider project story, the technical details don’t need to be at the forefront. What is vital is that that the project can articulate change processes both in technical and human work-flow terms.
Each project in the programme undertook an extensive base-lining exercise to identify the processes and systems (human and technical) involved in the curriculum design process ( the PiP Process workflow model is a good example of the output of this activity).
Most projects agreed that this activity had been really useful in allowing wider conversations around the curriculum design and approval process, as there actually weren’t any formal spaces for these types of discussions. In the session there was also the feeling that actually, technology was the trojan horse around which the often trickier human process issues could be discussed. As with all educational technology related projects all projects have had issues with language and common understandings.
So what are the successful techniques or “stories” around communicating technical changes? Peter Bird and Rachael Forsyth from the SRC project shared their experiences with using and external consultant to run stakeholder engagement workshops around the development of a new academic database. They have also written a comprehensive case study on their experiences. The screen shot below captures some of the issues the project had to deal with – and I’m sure that this could represents views in practically any institution.
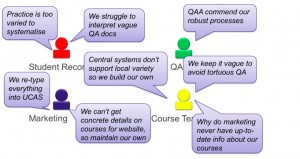
MMU have now created their new database and have a documentation which is being rolled out. You can see a version of it in the Design Studio. There was quite a bit of discussion in the group about how they managed to get a relatively minimal set of fields (5 learning outcomes, 2 assessments) – some of that was down that well known BOAFP (back of a fag packet) methodology . . .
Conversely, the PALET team at Cardiff are now having to add more fields to their programme and module forms now they are integrating with SITS and have more feedback from students. Again you can see examples of these in the Design Studio. The T-Sparc project have also undertaken extensive stakeholder engagement (in which they used a number of techniques including video which was part of another break out session) and are now starting to work with a dedicated sharepoint developer to build their new webforms. To aid collaboration the user interface will have discussion tabs and then the system will create a definitive PDF for a central document store, it will also be able to route the data into other relevant places such as course handbooks, KIS returns etc.
As you can see from the links in the text we are starting to build up a number of examples of course and module specifications in the Design Studio, and this will only grow as more projects start to share their outputs in this space over the coming year. One thing the group discussed which the support team will work with the projects to try and create is some kind of check list for course documentation creation based on the findings of all the projects. There was also a lot of discussion around the practical issues of course information management and general data management e.g. data creation, storage, workflow, versioning, instances.
As I pointed out in my previous post about the meeting, it was great to see such a lot of sharing going on in the meeting and that these experiences are now being shared via a number of routes including the Design Studio.
Widget Bash – what a difference two days make
“I got more more done here in a day than I would have in three or four days in the office”. Just one of the comments during the wrap up session at our widget bash (#cetiswb).
And judging from other comments from the other delegates, having two days to work on developing “stuff” is one of the best ways to get actually move past the “oh, that’s interesting, I might have a play with that one day” stage to actually getting something up and running.
The widget bash was the latest in our series of “bash” events, which began many years ago with code bashes (back in the early days of IMS CP) and have evolved to cover learning design with our design bashes. This event was an opportunity to share, explore and extend practice around the use of widgets/apps/gadgets and to allow delegates to work with the Apache Wookie (Incubating) widget server which deploys widgets built to the W3C widget specification.
We started with a number of short presentations starting with presentations from most of the projects in the current JISC funded DVLE programme. Starting with the rapid innovation projects, Jen Fuller and Alex Walker gave an overview of their Examview plugin, then Stephen Green from the WIDE project, University of Teeside explained the user centred design approach they took to developing widgets. (More information on all of the rapid innovation projects is available here). We then moved to the institutionally focused projects staring with Mark Stubbs from the W2C project who took us through their “mega-mash up” plans. The DOULS project was next with Jason Platts sharing their mainly google based approached. Stephen Vickers from the ceLTIc project then outlined the work they have been doing around tools integration using the IMS LTI specification. We also had a remote presentation around LTI implementation from the EILE project. Rounding up the DVLE presentations, Karsten Lundqvist from the Develop project shared the work they have been doing primarily around building an embed video BB building block. Mark Johnson (University of Bolton) then shared some very exciting developments coming from the iTEC project where smartboard vendors have implemented wookie and have widget functionality embedded in their toolset allow teachers to literally drag and drop collaborative activities onto their smartboards at any point during a lesson. Our final presentation came from Alexander Mikroyannidis on the ROLE project which is exploring the use of widgets and developing a widget store.
After lunch we moved from “presentation” to doing “mode”. Ross Gardler took everyone through a basic widget building tutorial, despite dodgy wifi connections and issues of downloading the correct version on Ant, most people seemed to be able to complete the basic “hello world” tutorial. We then split into two groups, with Ross continuing the tutorials and moving creating geo- location widgets and Scott Wilson working with some of the more experienced widget builders in what almost become a trouble shooting surgery. However his demo of repackaging a pac-mac game as W3C widget did prove very popular.
The sun shone again on day two and with delegates more familiar with wookie and how to build widgets, and potential applications for their own contexts, the serious bashing began.
One of the great things about working with open source projects such as Apache Wookie (Incubating), is the community sharing of code and problem solving We had a couple of really nice examples of this in action, starting with the MMU drop in pc-location widget. The team had managed to work out some IE issues that the wookie team were struggling with (see their blog post), and inspired by the geo-location templates Ross showed on day 1, managed to develop their widget to include geo-location data. Now if users access the service from a geo-location aware device it will return a list of free computers nearest to their real-time location. The team were able to successfully test this on ipad, galaxy tab, iphone and android phone. For non-location aware devices the service returns an alphabetical list. You can try it out here.
Sam Rowley and colleagues from Staffordshire university decided to work on some DOM and jQuery and issues. Whilst downloading the wookie software they noticed a couple of bugs, so they fixed them and submitted a patch to the Wookie community.
Other interesting developments emerged from discussions around ways of getting data out of VLEs. The team from Strathclyde realised that by using the properties settings in wookie they could pass a lot of information fairly easily from Moodle to a widget. On day two they converted a Moodle reading list block to a wookie widget with an enhanced interface allowing users to specify parameters (such as course code etc). The team have promised to tidy up the code and submit to both the wookie and moodle communitys. Inspired by this Stephen Vickers is going to have a look at developing a powerlink for webCT/BB with similar functionality.
On a more pedagogical focus some of the members of the Coeducate project worked on developing a widget version of the the 8LEM inspired Hybrid Learning Model from the University of Ulster. By the end of the second day they were well on the way to developing a drag and drop sequencer and were also exploring multiuser collaboration opportunities through the google wave api functionality which wookie has adopted.
Overall there seemed to be a really sense of accomplishment from delegates who managed to do a huge amount despite having to fight with very temperamental wifi connections. Having two experts on hand proved really useful to delegates as they were able to ask the “stupid” and more often than not, not so stupid questions. Having the event run over two days also seemed to be very popular as it allowed delegates to actually move from the thinking about doing something to actually doing it. It also highlighted the positive side of contributing to an open-source community and hopeful the Apache Wookie community will continue to see the benefit of increased users from the UK education sector. We also hope to run another similar event later in the year, so if you have any ideas or would like to contribute please let me know.
For another view of the event, I’ve also created a storify version of selected tweets from the event.
IMS Global Learning Consortium announces release of Common Cartridge v1.1
IMS has announced the final release of Common Cartridge v1.1.
According to the press release: “The Common Cartridge standard provides a means for interoperability, reusability, and customization of digital learning content, assessments, collaborative discussion forums, and a diverse set of learning applications. The standard offers both end-users and vendors the possibility of greater choice in both content and platforms. This latest version of Common Cartridge includes support for Basic Learning Tools Interoperability which provides a standard way of integrating rich learning applications or premium content with platforms such as Learning Management Systems, portals, or other systems.”
The standard is available for download from the IMS website.
Google Apps for Education UK User Group
Yesterday I attended the Google Apps for Education UK User Group meeting at the University of Loughborough. Organized by Martin Hamilton, the day provided a really useful update and insight into how google apps are being used throughout the education system, from primary schools to Universities.
Though the day was focused on google, the presentations, discussions, tweets did show an increasing demand from educators for more flexible, easy to use systems that just do what you want them to and are either free or have little cost. Google do seem to provide an awful lot (including jelly beans and rubik cubes). However they’re not the only game in town. But they do have awfully deep pockets, and I did have an overwhelming Pinky and the Brain sensation (what shall we do tonight, the same thing we do every night try to take over the world) but they have a much more successful strategy than my cartoon friends.
To give you a flavour of demo’s and discussion that took place over the day, I’ve collated some of the tweets into my story of the event.