What standards did projects intend to use to describe and package their OERs? – what other standards are in use? This is a post in the UKOER 2 technical synthesis series.
[These posts should be regarded as drafts for comment until I remove this note]
Descriptive choices
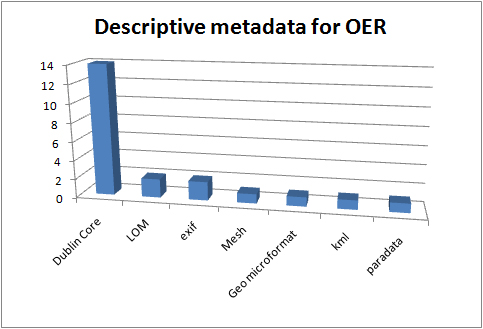
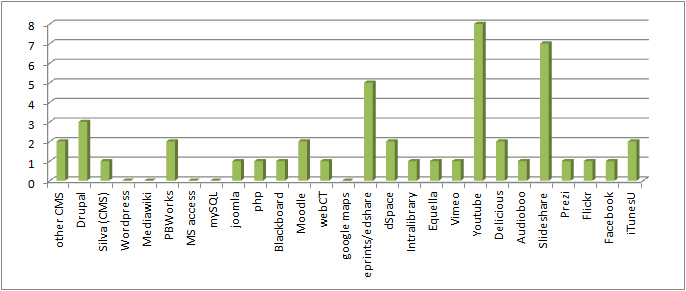
Descriptive metadata in use in the UKOER 2 programme
Dublin Core
“The Dublin Core Metadata Initiative “popularized the idea of “core metadata” for simple and generic resource descriptions” and its initial 15 descriptive elements became an international standard and a component of the Open Archives Initiatives Protocol for Metadata Harvesting. The Dublin Core community has subsequently developed in two directions – one developing application profiles to support particular implementation communities and the other developing in a way that would make its data structures more compatible with RDF and support the uptake of Dublin Core around Linked Data (http://dublincore.org/metadata-basics/). At this time there is, therefore, a very wide spectrum of usage of Dublin Core.” (http://blogs.cetis.org.uk/johnr/2010/03/17/the-use-of-dublin-core-metadata-in-the-ukoer-programme/)
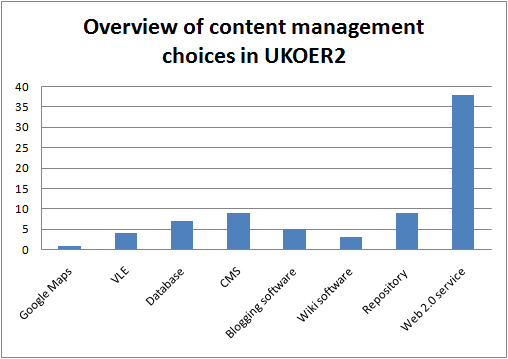
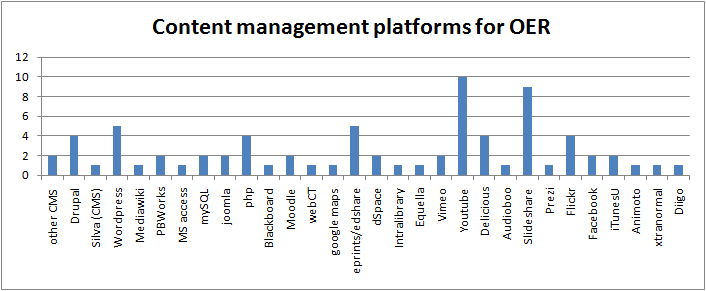
As in the first UKOER programme Dublin Core metadata is by far the most widely used descriptive standard in the programme. As in that programme, it is not clear what version of Dublin Core metadata projects are using (many are likely to be using some form of the basic DC Metadata Element Set, some may be using the newer DC Metadata Terms structure), nor is it clear if there is any common set of metadata element choices in use (the programme’s descriptive requirements are representable in Dublin Core and this is likely to form a common set, but there are other valid ways to present this information)
As noted in commenting on the first UKOER programme, many projects will be using Dublin Core because it is probably the most commonly implemented interoperability standard in repositories and is also a required part of the OAI-PMH protocol.
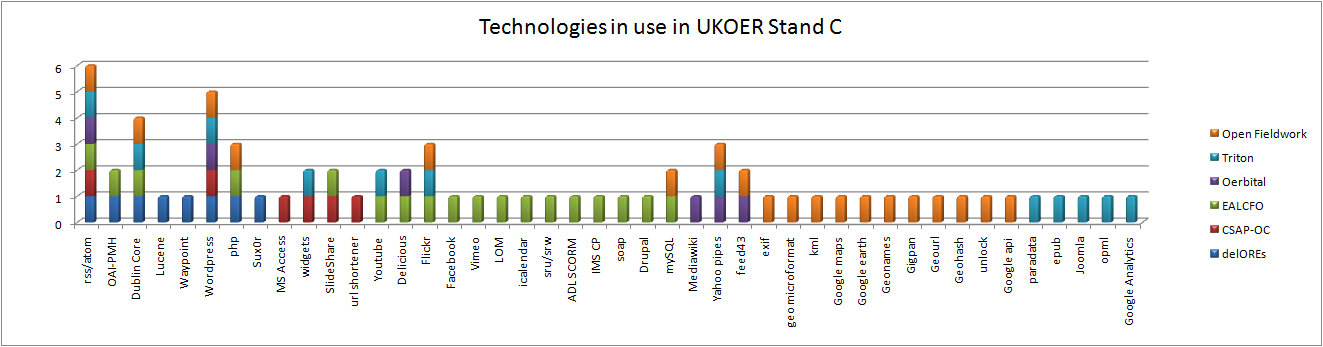
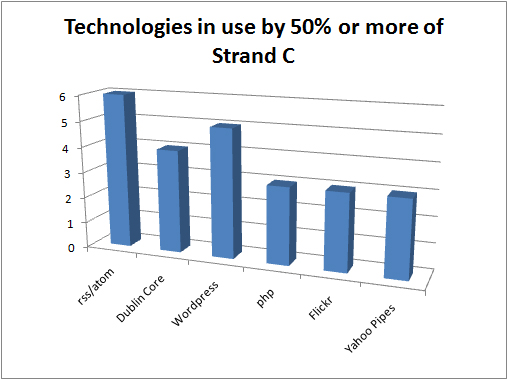
It is, however, noteworthy that some of the projects are developing a wordpress plugin to support the creation of DC metadata based on items in blog posts rather than the blog post itself (for more details please refer to the Summary of Strand C [forthcoming]) .
IEEE LOM
““Learning Object Metadata (LOM) is a data model, usually encoded in XML, used to describe a learning object and similar digital resources used to support learning. The purpose of learning object metadata is to support the reusability of learning objects, to aid discoverability, and to facilitate their interoperability, usually in the context of online learning management systems (LMS).”http://wiki.cetis.org.uk/What_is_IEEE_LOM/IMS_LRM
The LOM standard is available from the IEEE store. There are also many Application Profiles of the LOM data model. One of which is the UK LOM CORE http://www.cetis.org.uk/profiles/uklomcore/uklomcore_v0p3_1204.doc ” ( http://blogs.cetis.org.uk/johnr/2010/03/11/the-use-of-ieee-lom-in-the-ukoer-programme/)
The use of IEEE LOM in the second programme is quite a bit lower than in the first UKOER programme. Two possible reasons for this are: 1) fewer projects are using learning object repositories so there is less native support for LOM 2) in the first programme a number of HEA subject centres may have had significant quantities of existing content in the LOM which they released under an open licence, in the second programme projects may not have had relevant legacy content in this form. [Note: these are speculative].
exif
Exif is a standard widely used in cameras and smartphones for storing and transferring information about images, audio, and associated tags. More information is available in the Wikipedia article.
In use by the Open Fieldwork and ORBEE projects.
MeSH
MeSH (Medical Subject Headings ) is not a descriptive metadata standard as such but it is rather a controlled vocabulary used in the description of medical resources. It can be used and referenced with a number of metadata standards such as Dublin Core and IEEE LOM.
In use by the PORSCHE project.
Geo Microfromat
“geo (pronounced “gee-oh”) is a simple format for marking up WGS84 geographic coordinates (latitude; longitude), suitable for embedding in HTML or XHTML, Atom, RSS, and arbitrary XML. geo is a 1:1 representation of the “geo” property in the vCard standard (RFC2426) in HTML, one of several open microformat” from http://microformats.org/wiki/geo.
In use by the Open Fieldwork project.
KML
Keyhole Markup Language: “KML is an XML language focused on geographic visualization, including annotation of maps and images. Geographic visualization includes not only the presentation of graphical data on the globe, but also the control of the user’s navigation in the sense of where to go and where to look.” The major implementation of this standard is in Google Earth and Google Maps.
In use by the Open Fieldwork project.
paradata
Paradata is a rapidly evolving specification to describe activity and review data for digital assets. The initial specification was developed by the NSDL) in connection with the US Learning Registry initiative.
In conjunction with SRI International the Oerbital project developed an experimental template to generate paradata from mediaiwki pages at the OER Hackday.
Packaging choices
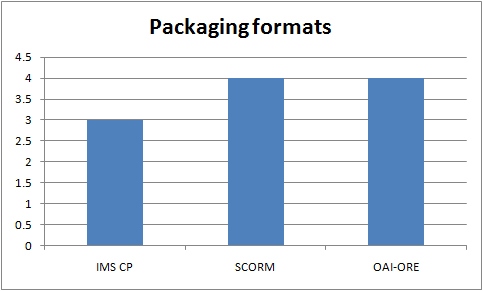
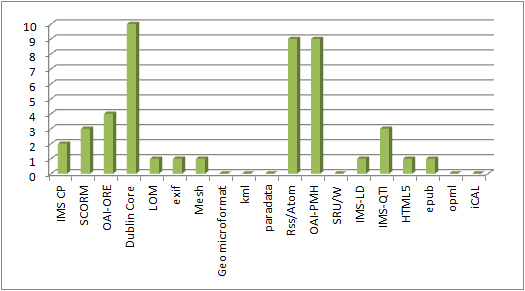
Packaging formats in use in the UKOER 2 programme
IMS CP
“IMS Content Packaging “describes data structures that can be used to exchange data between systems that wish to import, export, aggregate, and disaggregate packages of content.”http://www.imsglobal.org/content/packaging/ .” (http://blogs.cetis.org.uk/johnr/2010/03/08/the-use-of-ims-cp-in-the-ukoer-programme/)
ADL SCORM
““The Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM) integrates a set of related technical standards, specifications, and guidelines designed to meet SCORM’s high-level requirements—accessible, interoperable, durable, and reusable content and systems. SCORM content can be delivered to your learners via any SCORM-compliant Learning Management System (LMS) using the same version of SCORM.” (http://www.adlnet.gov/Technologies/scorm/default.aspx )” (http://blogs.cetis.org.uk/johnr/2010/04/01/the-use-of-adl-scorm-in-the-ukoer-programme/)
Two projects are using both IMS Content Packaging and ADL SCORM – EALFCO and ALTO. ALTO’s use may relate to the capabilities of the tools they have chosen to use.
OAI-ORE
““Open Archives Initiative Object Reuse and Exchange (OAI-ORE) defines standards for the description and exchange of aggregations of Web resources.” (http://www.openarchives.org/ore/)””
OAI-ORE – a number of projects mentioned this standard. For three of the four projects the standard is supported out of the box by the repository platform they were using and it is there is no indication of actual or intended use. Part of the OSTRICH project team (the partners at University of Bath) were investigating the possible use of OAI-ORE with their repository.
Other content related standards in use
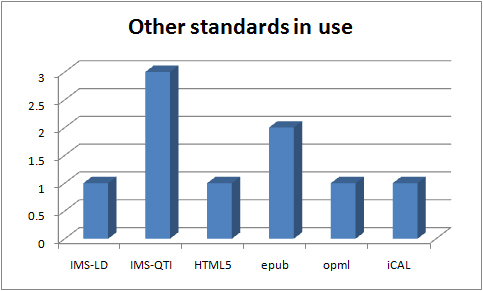
Other assorted standards in use in the UKOER 2 programme
The other standards graph is a miscellanea of other standards which projects are using which are distinctive but don’t easily fit into other categories.
IMS LD
The IMS Learning Design specification provides a flexible markup language to encode pedagogies (http://www.imsglobal.org/learningdesign/)
The ALTO project is usingconcepts and structures from IMS-Learning Design to inform their work but they are NOT implementing the specification
IMS QTI
“IMS Question & Test Interoperability Specification http://www.imsglobal.org/question/ is a standard used to support the interoperability and exchange of digital assessment items (questions, answers, and data).” (http://blogs.cetis.org.uk/johnr/2010/03/03/the-use-of-ims-qti-in-the-ukoer-programme/)
IMS QTI, one of the content types whose release surprised us in the first UKOER programme, has again been released by a number of projects (De-Stress, OER Cafe, Ripple).
HTML5
HTML5 is a work in progress of the latest update to HTML the defining specification of the world wide web.
The De-Stress project used this specification.
epub
“EPUB is a distribution and interchange format standard for digital publications and documents.” http://idpf.org/epub
Although mobile delivery and etextbooks were not an explicit part of the call both DHOER and Triton are experimenting with the epub format to explore these options.
OPML
OPML (Outline Processor Markup Language) http://www.opml.org/spec is being used in the progamme by the Triton project to support exchanging lists of RSS feeds.
iCalendar
the iCalendar specification is an exchange format for calendar information which can be used to record diary information or request meetings.
The EALFCO project was investigating the use of this specification.