This is just a quick test to illustrate the new embed feature of LAMS sequences. You can now get embed code for sequences from the LAMS Community site. You should be able to preview this sequecce, and edit it using LessonLAMS if you have an account. A great step forward from the LAMS team.
Social Media and Academia
Glasgow is one of the participating cities in the global Social Media Week. I was pleased to be able to attend the Social Media and Academia workshop at Glasgow University earlier this week; organised by Edinburgh Beltane, Beacon for Public Engagement and EDINA.
The event generated a really interesting discussion around use of social media from three main perspectives – teaching and learning, the library and community engagement. Nicola Osbourne (@suchprettyeyes) live blogged during the session and her account really captures the varied discussion that took place.
The things that struck me most were around the power to use social media to connect (or perhaps) reconnect place and community. Being a bit of a transient soul, I tend to use and think of social networks as virtual space devoid of location. However a sense of place is important for institutions, and it was interesting to hear about the various uses of Facebook within Glasgow University and also the discussion around the dangers of being in too many networks – particularly related to staff time to monitor these networks for any request for information. We also heard form Chris Speed and Peter Matthews about a really fascinating project in Wester Hailes, Edinburgh, were local residents are sharing their memories of places, and place through voice memories via social networks – in this case primarily Facebook. I also found out about how Oxfam are using tagging of objects so you can now trace things you donate and see how much money they have been sold for.
There also seems to be a growing recognition in academia of the power of social networks – are we, in Gartner terms, on the slope of enlightenment perhaps?
I’ve also pulled together some of the tweets from the session too – which gives more of a twittter stream of conscious feel for the session too. All in all a really thought provoking session which I’m still thinking through. Many thanks to EDINA and Beltane for organising the session and to colleagues at Glasgow Uni for hosting it.
How would you build a widget authoring tool?
Yesterday along with about 20 others I attended a Design Event organised by the Widg@t project, which is being funded through the current round of JISC Learning Teaching Innovation Grants (LTIG).
The aim of the day was to help the team “define the design specification for the WIDGaT toolkit, in particular the Design Decision Maker and Authoring Tool interface.” The team are planning to build a tool specifically aimed at non-techies – ” The WiDGaT toolkit (Design Decision Maker, Authoring Toolkit) aims to enable staff or students without technical expertise to easily design, develop and share widgets that support personalised learning. It enables the creation of widgets that address particularly (but not exclusively) the needs and preferences of disabled students.”
Splitting into small groups, the morning session was designed to get us thinking not about the authoring tool, but rather on designing widgets. Using the paper based design process the team had used during their previous WIDE project (see my previous post on this), each group had to create a design specification for a widget. The picture gives an idea of how the group I was in used the Design templates and flip chart to record our ideas.

widgat design template
The afternoon was then spent thinking about what kind of tool would allow people without any development experience build our, or indeed any other, widget. So we were thinking around a set of questions including:
*What would be the best way to replicate the f2f, paper supported, decision making process we had gone through?
*What kinds of interface, components and services would need to be available?
*Would templates be viable/useful?
*How would you save/share/publish outputs?
The group I was in spent quite a bit of time discussing the need to include some of the information made explicit in the Design template sheets e.g. detailed “personna” and “scenario” (basically the who, why and how of widget use). Although fully appreciating the need for them, we did wonder if they are better done offline, and if too much pre-authoring form filling might be off putting and actually slightly counter productive? We were also concerned with scope creep and very aware that the team are working to a tight timescale for development. So again we spent quite a bit of time discussing how to create an environment that gave enough options to be useful/useable, extensible to allow new functionality to be easily integrated and also, most importantly, was feasible to build.
During the feedback session it was clear that everyone in the room was broadly thinking in a similar way – particularly around the pragmatics of building a working system within the project timescale. The use of templates was also popular, as that provides a way to show users what is possible and also define an initial set of components/services.
I found the day to be very stimulating and very well structured, so thanks to all the team for their efforts in planning. As with any well designed design process, our input doesn’t stop after one day. The team are now pulling together all the ideas, reflecting on the themes emerging from the day and are going to produce a draft specification which we will be asked to feedback on before producing their final specification. I’m really looking forward to seeing how the toolkit develops and enjoying being part of a collaborative, user centred design process.
Design bash 11 pre-event ponderings and questions
In preparation for the this year’s Design Bash, I’ve been thinking about some of the “big” questions around learning design and what we actually want to achieve on the day.
When we first ran a design bash, 4 years ago as part of the JISC Design for Learning Programme we outlined three areas of activity /interoperability that we wanted to explore:
*System interoperability – looking at how the import and export of designs between systems can be facilitated;
*Sharing of designs – ascertaining the most effective way to export and share designs between systems;
*Describing designs – discovering the most useful representations of designs or patterns and whether they can be translated into runnable versions.
And to be fair I think these are still the valid and summarise the main areas we still need more exploration and sharing – particularly the translation into runnable versions aspect.
Over the past three years, there has been lots of progress in terms of the wider context of learning design in course and curriculum design contexts (i.e. through the JISC Curriculum Design and Delivery programmes) and also in terms of how best to support practitioners engage, develop and reflect on their practice. The evolution of the pedagogic planning tools from the Design for Learning programme into the current LDSE project being a key exemplar. We’ve also seen progress each year as a directly result of discussions at previous Design bashes e.g. embedding of LAMS sequences into Cloudworks (see my summary post from last year’s event for more details).
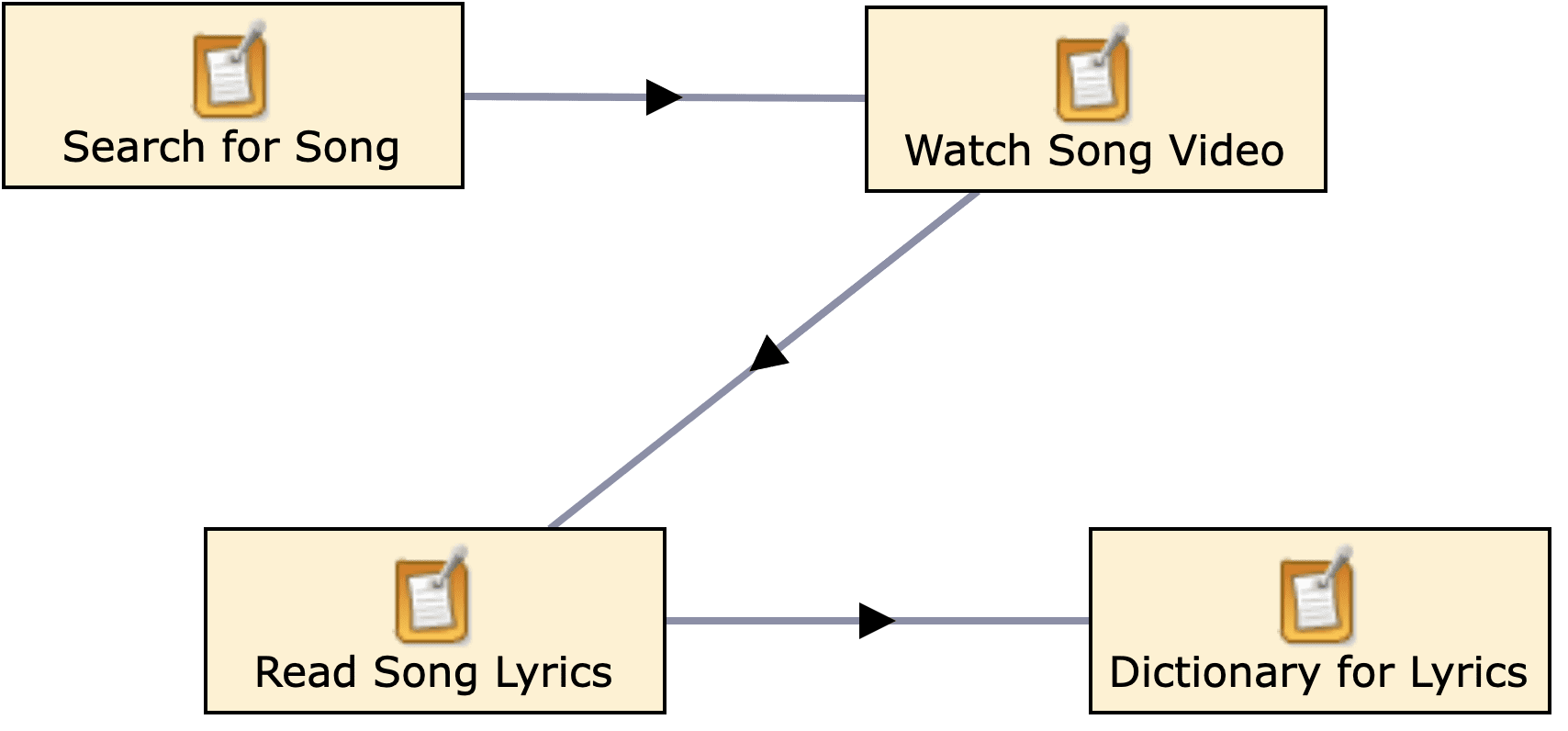
The work of the Curriculum Design projects in looking at the bigger picture in terms of the processes involved in formal curriculum design and approval processes, is making progress in bridging the gaps between formal course descriptions and representations/manifestations in such areas as course handbooks and marketing information, and what actually happens in the at the point of delivery to students. There is a growing set of tools emerging to help provide a number of representations of the curriculum. We also have a more thorough understanding of the wider business processes involved in curriculum approval as exemplified by this diagram from the PiP team, University of Strathclyde.
PiP Business Process workflow model
Given the multiple contexts we’re dealing with, how can we make the most of the day? Well I’d like to try and move away from the complexity of the PiP diagram concentrate a bit more on the “runtime” issue ie transforming and import representations/designs into systems which then can be used by students. It still takes a lot to beat the integration of design and runtime in LAMS imho. So, I’d like to see some exploration around potential workflows around the systems represented and how far inputs and outputs from each can actually go.
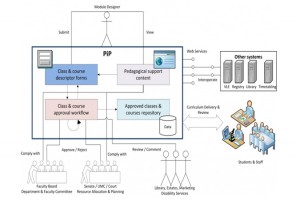
Based on some of the systems I know will be represented at the event, the diagram below makes a start at trying to illustrates some workflows we could potentially explore. N.B. This is a very simplified diagram and is meant as a starting point for discussion – it is not a complete picture.
Design Bash Workflows
So, for example, starting from some initial face to face activities such as the workshops being so successfully developed by the Viewpoints project or the Accreditation! game from the SRC project at MMU, or the various OULDI activities, what would be the next step? Could you then transform the mostly paper based information into a set of learning outcomes using the Co-genT tool? Could the file produced there then be imported into a learning design tool such as LAMS or LDSE or Compendium LD? And/ or could the file be imported to the MUSKET tool and transformed into XCRI CAP – which could then be used for marketing purposes? Can the finished design then be imported into a or a course database and/or a runtime environment such as a VLE or LAMS?
Or alternatively, working from the starting point of a course database, e.g. SRC where they have developed has a set template for all courses; would using the learning outcomes generating properties of the Co-genT tool enable staff to populate that database with “better” learning outcomes which are meaningful to the institution, teacher and student? (See this post for more information on the Co-genT toolkit).
Or another option, what is the scope for integrating some of these tools/workflows with other “hybrid” runtime environments such as Pebblepad?
These are just a few suggestions, and hopefully we will be able to start exploring some of them in more detail on the day. In the meantime if you have any thoughts/suggestions, I’d love to hear them.
Summer round up from the institutional DVLE projects
Summer generally provides a bit of time for reflection and gathering of thoughts. It also marks the start of the final phase of the current JISC Distributed Virtual Learning Environments (DVLE) programme. For the five institutionally based projects, this summer has provided a short break before some major implementations and evaluations get underway in the new semester. This post summarizes some of the developments and future plans as outlined by the projects in their recent interim reports.
To give a bit more context the original call for funding for the institutional projects specifically asked for bids that would:
” . . .review their virtual learning environment and related systems to establish to what extent they meet the current and projected needs of the wide range of users in the institution and beyond, and implement technical work to widen the range of functionality the VLE can provide in an interoperable way.”
Which would lead to a set of deliverables including:
“• Enhancing the flexibility of VLEs to meet new and developing user requirements and to permit future expansion and changes.
• Demonstration of a range of architecture models for composing institutionally delivered learning environments.
• Guidance on, and models for, expanding VLE functionality and delivering it in different ways to meet institutional needs.
• An increased number of high-quality sharable widgets and applications made available to common web platforms in UK institutions, and an easier process of deploying them.”
So what progress is being made?
ceLTIc, University of Edinburgh
Progress continues with deployment of LTI connectors across a range of platforms including BB, Pepplepad, Elgg. You can get more of a feel for what the project has achieved so far from their recent presentation at our IMS LTI and LIS in Action Webinar. The project are now entering their evaluation phase which aims to “explore the impact of the implementation of LTI connectors with a VLE and four applications: Elgg, WebPA, PebblePad and Learning Objects in a number of higher education institutions from the perspective of:
tutor; developer; e-learning support; administrator.” More information about the evaluation methodology can be found on the project blog.
DEVELOP, University of Reading
The DEVELOP (Developing and Enhancing Virtual Learning Environments and E-Learning Options) team at Reading have primarily been exploring the extension of their BlackBoard VLE to allow greater pedagogic flexibility and their portfolio provision so that it can be used for teaching and assessment purposes. Scoping documents for their widget development (Tagging and recommender, portfolio, ASSET Video, content) are available from the project blog. At the moment, the widgets are all at various stages of development and user testing. The user evaluation and testing are part of the rapid prototyping approach the team are using (you can read more about the technical evaluation part of this process in this post. These evaluations will form the basis for a set of case studies around the effectiveness of each of the widgets. The case studies will be based on the templates created at Reading as part of another project JISC funded project, OULDI, which is part of the Curriculum Design Programme. The team have also been working closely with their key internal technical stakeholders to ensure sustainability of developments. The University of Bedfordshire is also testing the video widget.
DOULS, OU
The DOULS (Distributed Open University Learning Systems) team have continued with key user engagement processes to scope, define and specify the set of Google gadgets they are going to develop: Assessment Helper; Forum Recommender; Forums; OU Buddy; Study Planner. Draft gadget functionality specs for each one is available the project blog. The team have also documented their process and have produced a number of useful guidelines relating to usability and accessibility in terms of testing gadgets and overall management of accessibility within a VLE. These are openly available from the blog. The team are continuing to learn the “ins and outs” of working with the Google Apps for Education API for widescale adoption. Again the team are sharing some of their “visions” for potential Google App/Moodle integration and thoughts around potential uses/extensions for the Google start page on the blog. There will be more code releases in September, when they will also start their evaluation. Their interim report is also available for download from the blog.
SLEP, University of Southampton
The SLEP (Southampton Learning Environment Prototype) project is part of a wider institutional wide initiative at Southampton to restructure both its research and teaching and learning environments. As you’d expect from Southampton, open and linked data are central to their approach and the team have used a “co-design” process “made up of a large- scale student survey, smaller focus groups and one-on-one interviews) has revealed a preference for a small number of key services in our initial launch (including email and timetabling).” This process has also surfaced the importance of groups and communities, and the team’s prototype interface design highlights these and makes “ them the lens through which students and staff access all of the data and services of the institution”. The project is now coming out of “stealth” mode with their first round of apps being released in September accompanied by a large scale (c. 1,000 students) user evaluation of their new user interface. More detail on their overall approach and the co-design methodology is outlined in this paper presented at the PLE conference earlier this summer.
W2C, MMU
The W2C team continue to make good progress with what they often refer as their “megamash up”. The team have made steady progress developing web services including: PC Availability; Fee Status (RSS); WebCT Areas & Announcements (RSS); Library Reading Lists (RSS) & Podcasts (RSS); Integrating Talis Aspire and Equella. Providing this information in a mobile friendly way has had a dramatic impact on the number of hits these services are now getting. The team have been closely monitoring the usage of these services and shared how they collect the data and some of their insights in this post. The team have also been involved in a study of student use of mobile devices with a number of other institutions. Preliminary findings from the on the MMU part of the study are available in this post .
The team have prioritised the development of web services for mobile devices and have been working with oMbiel’s campusM mobile phone product. This has allowed them to rapidly deploy their web-services and create a user feedback loop. The team have also undertaken work in developing open source widgets for their Moodle installation which I’ll refer to later in this post. The W2C project, again is part of a wider institutional change process around provision of teaching and learning and the team have been very pro-active in sharing their “core- plus” model with the rest of the programme and the wider community.
Reflections
The CETIS Distributed Learning Environments briefing paper was a key starting point for the programme, and particularly for the institutional strand, JISC wanted to find out the key institutional infrastructure issues are surrounding more flexible creation distribution of apps/gadgets/widgets and how data can be shared and re-used effectively.
Again going back to the funding call: “ The following technical approaches are of particular interest:
• Widget platforms external to the VLE displaying content from a range of sources including the VLE.
• Plug-ins to the VLE or other institutional web platform demonstrating the use of open educational standards such as IMS LTI (learning tools interoperability).
• The VLE providing some of its data and functionality as widgets/and or plug-ins to be consumed in other environments.
• Enabling access to particular research equipment in VLEs via widgets.
• Identity and access management approaches, such as OAuth.
• Approaches which illustrate innovative creation, use and consumption of data sets (including linked data ) sets across multiple platforms.”
Security has been and continues to be a key concern for projects (as highlighted in this post from Mark Stubbs after the programme start up meeting last September). Accessibility is also a concern, and it’s probably fair to say that the DOULS and others at the OU have had to spend more time than they probably first envisaged ensuring that their Google apps provision met required accessibility guidelines.
However there have been some quick wins for example W2C have been able to accelerate their mobile app deployment using an external partner which freed up the team’s time to work on developing web-services. We are also beginning to get a far greater understanding of student mobile device ownership and indeed from all the user engagement across the projects a greater understanding of the key data/services which staff and students actually want and use regularly.
In terms of standards/ specifications we have a stalwart supporter of the IMS LTI approach from Stephen Vickers at the ceLTIC project who clearly thinks the IMS way is a win, win, win scenario. There is still some resistance to implementing LTI in other projects – partly due to their unfinished status. Reading are keeping a watching brief on developments and are concentrating on developing widgets they know will work in their VLE. Whereas Southampton prefer to work with more conventional, non education specific web service approaches. However the recent announcement from IMS that they are now merging the development of full and basic LTI into one specification may start to convince more potential adopters. Once again the security question raises its head. Whilst there seems to be more convergence across the IMS, Open Social and Wookie development communities around the use of services such as OAuth, and the development of data handling process which sh/could start to allay common concerns around security of sensitive data such as assessment information etc. However, there is still probably a need for quite a dramatic culture shift within institutional provision and access before OAuth is widely adopted across the sector.
The programme has also afforded the opportunity for projects to explore the W3C Apache Wookie (Incubating) approach to the building and deployment of widgets. Our widget bash provided hand on opportunities for developers to get started building (and repurposing their own apps) wookie widgets. Despite the (relative) ease of building widgets, there has been some articulation surrounding concerns around the institutional deployment of a wookie widget server see this post from the W2C project. There continues to be an appetite for a stable sandbox/test server that projects could experiment with. This has been discussed before through our widget working group (pre-cursor to the DVLE programme) and it is something we at CETIS do recognise. Unfortunately we aren’t in a position to guarantee stability of any such service, and so we have being advocating a community based solution (perhaps augmented with a bit of funding from JISC). This is bound to be something we return to at the end of the programme once the projects have completed their reviews of their approaches and we can get a more informed view from across the programme.
There is also the question of where widgets/apps/gadgets should be accessed from after the projects finish. Should the code be available only via project websites? Do we need think about developing education app store (again this brings up similar issues as the wookie test server). One potential interim measure we are starting to investigate is the use of the JISC Design Studio which is primarily being used to share outputs from the Curriculum Design and Delivery programmes, but there are plans to use it to share other programme outputs too.
In the final stage of the funding cycle, the projects will be reflecting more on their infrastructure and how they relate to the models outlined in the CETIS DLE briefing paper. Both DEVELOP and W2C are seeing alignment with Model 2 “plug-ins to existing VLEs”.

screen shot of DLE Model 2
W2C have begun to articulate their model in a some more detail in this post.
Over the coming months as evaluations begin in earnest, it will be interesting to see any convergences of approaches/models start to appear, and to explore what kind of affordances the projects distributed learning environments have to offer over traditional approaches.
More information about the projects and the programme support activities can be found on the CETIS wiki. There is also a public netvibes page with feeds from all the project blogs.
The timeline below also gives another view of programme activity through aggregated tweets using the programme hashtag #jiscdvle and with an RSS feed from the related Learning Platforms topic page on the CETIS website.
Betweenness Centrality – helping us understand our networks
Like many others I’m becoming increasingly interested in the many ways we can now start to surface and visualise connections on social networks. I’ve written about some aspects social connections and measurement of networks before.
My primary interest in this area just now is more at the CETIS ISC (innovation support centre) level, and to explore ways which we can utilise technology better to surface our networks, connections and influence. To this end I’m an avid reader of Tony Hirst’s blog, and really appreciated being able to attend the recent Metrics and Social Web Services workshop organised by Brian Kelly and colleagues at UKOLN to explore this topic more.
Yesterday, promoted by a tweet of a visualisation of the twitter community at the recent eAssessment Scotland conference, the phrase “betweenness centrality” came up. If you are like me, you may well be asking yourself “what on earth is that?” And thanks to the joy of twitter this little story provides an explanation (the zombie reference at the end should clarify everything too!)
View “Betweenness centrality – explained via twitter” on Storify
In terms of CETIS, being able to illustrate aspects of our betweenness centrality is increasingly important. Like others involved in innovation and community support, it is often difficult to qualify and quantify impact and reach, and we often have to rely on anecdotal evidence. On a personal level, I do feel my own “reach” an connectedness has been greatly enhanced via social networks. And through various social analysis tools such as Klout, Peer Index and SocialBro I am now gaining a greater understand of my network interactions. At the CETIS level however we have some other factors at work.
As I’ve said before, our social media strategy has raised more through default that design with twitter being our main “corporate” use. We don’t have a CETIS presence on the other usual suspects Facebook, Linkedin , Google+. We’re not in the business of developing any kind of formal social media marketing strategy. Rather we want to enhance our existing network, let our community know about our events, blog posts and publications. At the moment twitter seems to be the most effective tool to do that.
Our @jisccetis twitter account has a very “lite” touch. It primarily pushes out notifications of blog posts and events, we don’t follow anyone back. Again this is more by accident by design, but this has resulted in a very “clean” twitter stream. On a more serious note, our main connections are built and sustained through our staff and their personal interactions (both online and offline). However, even with this limited use of twitter (and I should point out here that not all CETIS staff use twitter) Tony has been able to produce some visualisations which start to show the connections between followers of the @jisccetis account and their connections. The network visualisation below shows a view of those connections sized by betweenness centrality.
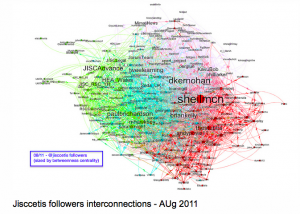
So using this notion of betweenness centrality we can start to see, understand and identify some key connections, people and networks. Going back to the twitter conversation, Wilbert pointed out ” . . . innovation tends to be spread by people who are peripheral in communities”. I think this is a key point for an Innovation Support Centre. We don’t need to be heavily involved in communities to have an impact, but we need to be able to make the right connections. One example of this type of network activity is illustrated through our involvement in standards bodies. We’re not at always at the heart of developments but we know how and where to make the most appropriate connections at the most appropriate times. It is also increasingly important that we are able to illustrate and explain these types of connections to our funders, as well as allowing us to gain greater understanding of where we make connections, and any gaps or potential for new connections.
As the conversation developed we also spoke about the opportunities to start show the connections between JISC funded projects. Where/what are the betweenness centralities across the e-Learning programme for example? What projects, technologies and methodologies are cross cutting? How can the data we hold in our PROD project database help with this? Do we need to do some semantic analysis of project descriptions? But I think that’s for another post.
My memory of eAssessment Scotland
Along with around another 270 people, attended the eAssessment Scotland Conference on 26 August at the University of Dundee. It was a thought provoking day, with lots of examples of some innovative approaches to assessment within the sector.
Steve Wheeler got the day off to a great start talking us through some of the “big questions” around assesment, for example is it knowledge or wisdom that we should be assessing? and what are the best ways to do this? Steve also emphasised the the evolving nature of assessment and the need to share best practice and introduced many of us to the term “ipsative assessment”. The other keynotes complemented this big picture view with Becka Coley sharing her experiences of the student perspective on assessment and Pamela Kata showing taking us through some of the really innovative serious games work she is doing with medical students. The closing keynote from Donald Clark again went back to some of the more generic issues around assessment and in particular assessment in schools and the current UK governments obsession with maths.
There is some really great stuff going on in the sector, and there is a growing set of tools, and more importantly evidence of the impact of using e-assessment techniques (as highlighted by Steve Draper, University of Glasgow). However it does seem still quite small scale. As Peter Hartley said e-assessment does seem to be a bit of a cottage industry at the moment and we really more institutional wide buy in for things to move up a gear. I particularly enjoyed the wry, slightly self-deprecating presentation from Malcolm MacTavish (University of Abertay Dundee) about his experiments with giving audio feedback to students. Despite being now able to evidence the impact of audio feedback and show that there were some cost efficiencies for staff, the institution has now implemented a written feedback only policy.
Perhaps we are on the cusp a breakthrough, and certainly the new JISC Assessment and Feedback programme will be allowing another round of innovative projects to get some more institutional traction.
I sometimes joke that twitter is my memory of events – I tweet therefore I am mentality ![]() And those of you who read my blog will know I have experimented with the Storify service for collating tweets from events. But for a change, here is my twitter memory of the day via the memolane service.
And those of you who read my blog will know I have experimented with the Storify service for collating tweets from events. But for a change, here is my twitter memory of the day via the memolane service.
Socially favoured projects, real measures of engagement?
Martin Hawksey has been doing a bit of playing around with JISC project data lately and has now created a spreadsheet of the top “socially favoured” JISC funded projects.
As a large part of my job involves supporting and amplifying the work of JISC programmes, I’m also always looking for ways to keep in touch with projects between official programme meetings and feedback on reports. Over the past few years, I have personally found that twitter has been quite revolutionary in that regard. It gives me a flexible ‘lite” way to build relationships, monitor and share project developments. I’ve also noted how twitter is becoming a key dissemination tool for projects and indeed programmes. So I was fascinated to see Martin’s table and what sources he had used.
Like many others I’m becoming increasingly interested in the numerous ways that social services such as facebook, twitter, google+ etc can be used and analyzed. I’ve got my peer-index, checked out my klout – even this morning I had to have a look at twtrland to see what that service made of me. But I do take all of these with a pinch of salt, they give indication of things but not the whole picture.
For this exercise, Martin has used several sources of data including twitter, facebook, linked-in, google+, buzz, digg, delicious, stumbleupon. (See Martin’s post on how he did it). A number of things struck me on first looking at the spreadsheet. The top projects seemed to be related to “big” collections and repository focused. There wasn’t a lot from the teaching and learning side of things till around the mid 20s the Open Spires project, again though this is very much a content related project. Also the top projects all had high scores on the bookmarking sites. Facebook and Linked-In use seemed to be limited, but again the top projects all had relatively high scores. Twitter seemed to be the most consistently used service across the board. And perhaps most striking, after the top twenty or so use of all the services decreases dramatically.
So what does this all mean? Is the fact that the top ranked projects have high bookmarking scores mean that the projects actively encourage sharing in this way – or is it down to the already web-savvy habits of their users? Checking the first couple of projects, it’s hard to tell. The first 2 don’t have any obvious links/buttons to any of the “ranked services”, but the 3rd one has a google sharing app on its front page, and others have obvious links to facebook, twitter etc. I think there would almost need to be a follow up mini-report from each project on their assessment of the impact of these services to start to be able to make any informed comment. What impact does using social services have on sustainability? Does having a facebook page make a project more likely to maintain an up to date web site as per grant funding (see Martin’s post on this too)? Another point of note is that the links for a number of the top ranked projects go to generic and not project specific websites.
I’m not sure I’ve come to any conclusions about this, as with any data collection exercise it has raised more questions that it has answered, and the ranking it provides can’t be judged in isolation. For me, it would be interesting enhance the data to identify what programmes the projects have been funded from and then start to explore the evidence around the effectiveness of each of the social channels. However, it is fascinating to see another example of the different ways people can now start pulling “social” statistics together. Thanks Martin!
#dbash11
Following on from previous successful events, I’m pleased to announce that on 30 September we are once again running a Design Bash at the University of Oxford.
As in previous years this event will be very hands on allowing people to share their learning designs, tools and systems and to explore potential collaborations. Once again, we’ll be using Cloudworks to share resources and activity on the day. This year we hope to extend out from our core learning design community to involve those involved with building and using tools and standards dealing with course information, describing learning opportunities (xcri), and competencies e.g. Co-gent.
We’re also experimenting with the Eventbright system for registrations which allows me to put a neat little registration widget in this post. So, if you want to come along, just click the registration button below. As ever the event is free to attend and lunch and refreshments will be provided.
I’ll be posting more information about the agenda etc over the coming weeks too.
Words and pictures from “Advances in open systems for learning resources” workshop
Twitter story from the Advances in open systems for learning resources workshop, hosted by CETIS as part of the Repository Fringe 2011 conference.
View “Advances in open systems for learning resources”