The JISC Developing Digital Literacies programme is now well underway. As I reported from the programme start up meeting last October , the aim of this 2 year programme is too
” . . .promote the development of coherent, inclusive and holistic institutional strategies and organisational approaches for developing digital literacies for all staff and students in UK further and higher education.”
with projects:
” . . .working across the following stakeholder groupings in their plans for developing digital literacies: students, academic staff, research staff, librarians and learning resources and support staff, administrators and managers and institutional support staff . . .”
As part of the programme support project, over the last couple of months I’ve conducting our usual technical audits with the projects to get a picture of what technologies and standards they are using/considering to use at this stage. The results of these conversations are recorded in our PROD database.
The projects are due to complete their baselining phase at the end of January, so it has been timely to discuss some of the wider issues around using various technologies with each of the projects. The rest of this post gives a snap shot of the range of technologies the projects are currently using. NB Unfortunately I haven’t been able to speak with the UCL team, but once they have completed their baseline report we will be meeting and I’ll update the data, however don’t expect the general trends outlined in this post to change much.
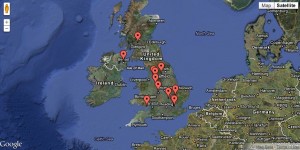
The map shows the locations of the 12 projects, with links to the prod entry for each. As the programme progresses, I’ll be adding a links to the design studio pages for each project too.
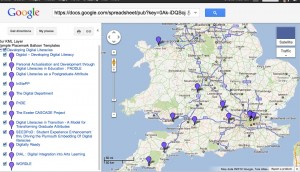
Map showing locations of DDL projects
The mindmap below gives an alternative view of the data entries for each project (if you click on the picture it will take you to a live version, NB the mind map will be open so you may find it easier to close nodes before exploring it in full).
The focus of the programme is more on the effective use of technology rather than as with other JISC funded work, the development of technology. On saying that, there are a couple of projects who are planning to develop some mobile applications and there are strong links between the work of the W2C project at MMU in relation the provision of mobile services, particularly with the SEEDPod project, University of Plymouth who have been working with MMU in conducting surveys of students uses of mobile devices. There are a number of approaches to mobile provision. The Developing Digital Literacy as a Post Graduate Attribute project is providing students with ipods to record and share their learning journeys, and to some extent leaving it to the students to find what works/doesn’t work for them. Whereas other projects (SEEDPod, InStePP) are developing more holistic, device and location agnostic approaches to provision of services/content.
So far we have 94 individual technologies and standards. The wordle below gives an overview.

Wordle of technologies & Standards in DDL progamme (Jan '12)
This bubblegram gives another view of the range and instances of technologies and standards. Again if you click on the picture you’ll go to a larger, interactive version.
The projects area all blogging (you can access aggregated feeds here) and WordPress is top of our chart with 8 projects using it, the majority of these are also using institutionally hosted versions. What is also noticeable, is the (relatively) high instances of non- institutionally based services such a social networking sites – particularly twitter and Facebook. At the moment the main (and anticipated) use of both is for general project dissemination, however a number of projects are both to communicate with staff/students e.g. to get people involved in focus groups. The PADDLE project are planning to use existing facebook groups as collaboration/communication point with some of their focus groups.
Other external services such as drop-box (for document sharing), doodle for arranging meetings and a range of google apps (docs, calendar etc) are also being widely used. For the later there is a mix of institutional provision and more general use of, for example google docs for sharing project team related information. As with other programmes and the following a general sector wide trend, Moodle comes out as the most common VLE across the programme.
In terms of standards, the main focus was on packing formats with IMS CP, IMS CC and SCORM all getting one mention each. As we are still in early days, most projects haven’t got a clear idea of what format they will release any content in, however there was an overall interest in, and indeed knowledge of OER (i.e. the DIAL project is building on experiences from a previous UK OER project) and most projects expressed an desire to release any relevant content as OERs.
A number of projects (e.g. The Exeter Cascade Project, InStePP) are looking at greater integration of digital literacies into wider competency frameworks through for example making more explicit curriculum links to institutional graduate attributes; and also through working with other wider programme related stakeholders such as SCOUNL and ALT.
As mentioned earlier, projects are just coming to the end of their baselining work, and at this stage they are keen not to be prescriptive about the technologies they will be using, as they want to be as flexible as possible. Also, key to number of the projects is the exploration of the how, what, where and why of technology use (both hardware and software) of staff and students and then making appropriate interventions/recommendations for wider institutional policies.
When I repeat this exercise next year, I have a suspicion that there may be a subtle shift to more institutionally based services as more content will have been created and being used/shared within VLEs/repositories. As any changes to curriculum provision, and institutional policies, if not in place, will be fairly well scoped by then too. I am wondering if we will see, similar to the Curriculum Design programme, an increase in the use of Sharepoint for more formal documentation and a decrease in use of more informal sharing services such as drop box. At the moment there the project teams are using drop box primarily for the convenience of any time/where/device access.
One of the things I was curious about was if these projects would be more “literate” in their choices of technologies to use, and what would be the balance between use of institutionally based services and more general web based services. I don’t think I have an answer to the question, but I have seen a healthy sense of pragmatism displayed by all the projects in terms of their approaches.
I’ve had some really interesting discussions with projects (particularly Digitally Ready) around the definition of technology and what it was I really wanted to record i.e. everyday /commonplace technologies like email, calendars etc; was I interested in what the project team were using for project management or more what they were using for stakeholder engagement? In fact it’s all of the above – which probably goes some way to explaining the number of different technologies recorded to date. I feel it’s also worthwhile every now and again just stepping back and reflecting on how our expectations of peoples and projects use of technologies (JISC programme digital literacy perhaps?) have evolved. A few years ago, we’d be lucky if we got all projects to have a blog with more than 2 or 3 entries by the end of a programme – now, it’s one of the first things on a projects to do list, and most institutions provide some kind of hosted blogging service.
When we were developing PROD originally it was to record the tools, standards outputs and development processes of very technically focused projects. However as we’ve started to use it more widely across the JISC elearning programme, we’ve used it not just to record what projects are building, but the what, how and when of technologies projects are actually using. In the not so development focused projects such as DDL this is central. I think that this is starting to give us some real evidence of the diversity and commonality of approaches within and across programmes, and give us greater understanding of how actual use of technologies is being enabled and embedded both from the bottom up and top down.
As they move into the next phase of the programme it will be fascinating to see how the projects start to use the findings from their baselining and how that will impact on their next phase of development.